
Hello! I have long dreamed of my own small garden. And dreams, as they say, tend to come true.
And now you have at hand your own source of fresh fruit, but problems lurked here too. In the trees I began to notice rust.
I didn’t want my garden to die, so I turned to a familiar gardener for help. He recommended using Bordeaux fluid. And you know, this turned out to be a very effective tool. Want to learn how to make Bordeaux liquid? What components will be required for its preparation? I will describe all this in detail now.
The content of the article:
Bordeaux mixture: preparation, application
The appearance of the Bordeaux mixture in the practice of gardening and horticulture was preceded by ordinary chance.
At the end of the last century, a farmer from the French province of Bordeaux, apparently, accidentally mixed lime and copper sulphate (history is silent about which component he did not want to throw away) to spray his vineyards against downy mildew (mildew).
So, with the light hand of a French farmer, the Bordeaux mixture continues its victorious march around the globe and is now still actively used against the vast majority of fungal and many bacterial diseases of a wide range of plants that are useful to humans.
It is a protective contact fungicide. It is not effective against agricultural pests.
A solution of Bordeaux mixture is recommended to be used in two versions: early spring ("blue") spraying of fruit trees when their buds have not fully blossomed and are still at rest - a "green cone" (3-4% solution) and spraying during the growing season plants (1% solution).
If the order of mixing solutions with this recipe is changed, that is, milk of lime is poured into a solution of copper sulfate, the quality of the drug will be low; You can also not mix strong solutions of these components and pour a strong solution of copper sulfate in a weak solution of milk of lime. In these cases, spherical crystals form, which are easily washed off by precipitation.
With proper preparation, the Bordeaux liquid should be blue, characterized by a stable suspension of colloidal particles, a neutral or slightly alkaline reaction (the latter is preferable). The drug with an acid reaction is phytotoxic, and a strongly alkaline solution is poorly retained on plants.
To determine the reaction of the Bordeaux mixture, a blue litmus or phenolphthalein (purgen) piece of paper moistened with water is dipped in its solution (the first piece does not change its color, the second one acquires a reddish or crimson color). In the absence of indicator paper, a clean iron wire or nail is lowered into a solution of Bordeaux liquid (for 1-1.5 minutes).
The Bordeaux mixture is prepared immediately before use. It cannot be stored for more than a day, as its aging occurs and its components precipitate and crystallize.
Vitriol-lime mixture. How to cook, when and where to use
The appearance of the Bordeaux mixture in the practice of gardening and horticulture was preceded by ordinary chance. At the end of the last century, a farmer from the French province of Bordeaux, apparently, accidentally mixed lime and copper sulfate (history is silent about which component he did not want to throw away) to spray his vineyards against downy mildew (mildew).
The effect of this mixture against mildew of grapes was stunning for him.
So, with the light hand of a French farmer, the Bordeaux mixture continues its victorious march around the globe and is now still actively used against the vast majority of fungal and many bacterial diseases of a wide range of plants that are useful to humans. It is a protective contact fungicide. It is not effective against agricultural pests.
A solution of Bordeaux mixture is recommended to be used in two versions: early spring ("blue") spraying of fruit trees when their buds have not fully blossomed and are still at rest - a "green cone" (3-4% solution) and spraying during the growing season plants (1% solution).
DRY BORDER MIX, consisting, as indicated above, of copper sulfate (copper sulfate) and lime (calcium hydroxide), is used to prepare Bordeaux liquid. To achieve the highest possible effect of the Bordeaux mixture, you should pay attention to the rather specific preparation of its solution.
A wooden, glass or clay container is used in the work (metal utensils are not suitable for these purposes).
In another container, 100-150 g of lime is dissolved in a small amount of cold water, adding it in small portions until a creamy mass is obtained; bring the total amount of milk of lime to 1 liter
At the next stage, the solution of copper sulfate is slowly, with constant stirring, poured in a thin stream into pre-filtered milk of lime (both solutions must be cold before joining).
If the order of mixing solutions with this recipe is changed, that is, milk of lime is poured into a solution of copper sulfate, the quality of the drug will be low; You can also not mix strong solutions of these components and pour a strong solution of copper sulfate in a weak solution of milk of lime. In these cases, spherical crystals form, which are easily washed off by precipitation.
To determine the reaction of the Bordeaux mixture, a blue litmus or phenolphthalein (purgen) piece of paper moistened with water is dipped in its solution (the first piece does not change its color, the second one acquires a reddish or crimson color). In the absence of indicator paper, a clean iron wire or nail is lowered into a solution of Bordeaux liquid (for 1-1.5 minutes).
If an iron object is covered with a red coating (copper precipitates), then the reaction is acidic and milk of lime should be added to the solution. Before pouring into the sprayer, the resulting solution should be filtered through a clean hair sieve or a rare cloth. The Bordeaux mixture is prepared immediately before use.
It cannot be stored for more than a day, as its aging occurs and its components precipitate and crystallize. When preparing a 3% solution (for "blue" spraying) Bordeaux liquid 300 g of copper sulfate take 400 g of lime.
During the growing season, a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture is used on an apple tree, pear against scab, phyllostictosis, moniliosis and other leaf spots. In the fight against scab of apple and pear, the first treatment, for example, is carried out when the buds are pink, the second - after flowering, and the next - after 10-18 days as necessary.
On plums and cherries, the drug is effective against leaf spot (clusterosporiosis, curliness, coccomycosis, moniliosis) - no more than four treatments.
Bushes of currants and gooseberries are treated with a solution of the drug (2-3 treatments) to avoid leaf damage by anthracnose, septoria and rust. Processing raspberries and strawberries (before flowering and after harvesting) is carried out against leaf spotting.
Bordeaux mixture protects potatoes and tomatoes of open and protected soil from their many fungal and a number of bacterial diseases. On cucumbers of open and closed ground, melon and watermelons, treatments allow you to get away from anthracnose, olive spotting, and bacteriosis.
On beets (sugar, table, fodder) - from peronosporosis (downy mildew), cercosporosis, rust. Onion - from peronosporosis, rust and rot (3 treatments). On medicinal plants (including ginseng) - from leaf spots (1-2 treatments).
Bordeaux mixture is also actively used in the protection of numerous flower plants and ornamental shrubs from rust, various spots and other diseases (treatment before and after flowering). Bordeaux mixture is also notable for the fact that it is widely used in gardening and after harvesting.
Soap should not be added to Bordeaux liquid, even neutral, since this does not improve the wettability of the leaf surface. Bordeaux fluid is not used with other drugs, since it is not compatible with them.
It is not dangerous for beneficial insects and bees, but during spraying and in the next 5-6 hours, it is better to isolate bees from treated plants. Using a sprayer, Bordeaux liquid is applied to plants in accordance with established standards and terms.
Its effectiveness, like other drugs, depends on the correct period of its use. Processing should not be carried out with high dew and on those days when precipitation is possible.
It should be noted that in the popular science literature on plant protection provides more extensive information on the use of this drug in many crops, here we mainly touch on a number of small details related to the specificity of the preparation of the Bordeaux mixture.
Due to its high fungicidal activity, good visibility of the treatments and good retention on the leaves, Bordeaux mixture is a gentle preparation for plants and remains popular among consumers, despite the presence of seemingly more effective and easy to use modern fungicides.
How to make Bordeaux liquid - important points
The basis of Bordeaux fluid is a mixture of lime and copper sulphate, and to be precise, aqueous solutions of milk of lime and copper sulphate (not to be confused with iron sulphate, which is also used to treat garden plants).
One of the important points in the process of preparing the solution in question is that the medium in which the interaction of copper sulfate and alkali will occur should be alkaline.
If the Bordeaux liquid solution is prepared correctly, the blue precipitate should remain in suspension for quite some time. The actual formulation and composition for the preparation of a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid are as follows (based on the production of 10 liters of solution):
- copper sulfate 100 gr;
- quicklime 100 gr;
- water 8 l
These components must be diluted in different containers. For copper sulfate, you can take copper, wooden, glass or clay dishes. Dissolve it in 1 liter of warm water. We extinguish lime in another container also in 1 liter of water.
After both solutions are ready, pour the solution of copper sulfate in the milk of lime. For stirring, use a wooden stick. In the process, the volume must be brought to 10 liters. To do this, use clean water and at the same time constantly stir.
What difficulties may arise?
If the gardener does not have sufficient experience, then in the process of preparing this solution, some difficulties are possible. To prevent plants from getting burned, you need to check the reaction on litmus paper. If the paper turns blue, there is too much lime in the solution.
What is this talking about? And this suggests that such a solution is characterized by weak fungicidal properties. The sediment in such Bordeaux liquid will form rather quickly and it will be unevenly distributed over the surface during processing, which is not good.
In addition, with a large amount of lime, the solution will not adhere well to the stems and leaves. But litmus paper may turn red and say this will be an overabundance of copper sulfate. You need to know that it is impossible to use such a solution for plants, since it is toxic.
You may not have litmus paper. No problem. You can check the solution with a regular nail or even a knife. In the event that a red coating appears on the metal, this indicates an excess of copper sulfate (it appears on the metal) and that the solution is improperly prepared.
To reduce the acidity of Bordeaux liquid, a certain amount of milk of lime is added. Which quantity is determined empirically. With a properly prepared solution, the metal should not be coated with copper.
How long can I store?
In order to prepare Bordeaux liquid, we figured out.But what if after processing the plants there is a certain amount of solution left? In this case, you need to know that the solution must be used on the day when it is prepared. If you use it after a few days, then it becomes ineffective.
Bordeaux fluid must be handled with care. Using a 1% solution during the growing season, burns may appear on leaves and fruits. If we talk about the fruits, it looks like a brown mesh.
The phytotoxicity of the drug is enhanced in cool as well as rainy weather. Brown spots may also appear on the fruit. Burns are more dangerous for young fruits. The most sensitive to Bordeaux liquid are fruit trees such as cherries and apricots.
As for the preparation of Bordeaux liquid, after reading the material in this article, you can not only prepare this mixture yourself, but also protect your garden trees and shrubs from various pests and diseases.
How to prepare Bordeaux liquid
In the preparation of Bordeaux LIQUID, solutions of copper sulfate and lime milk are mixed. For the preparation of 10 l of 1% Bordeaux LIQUID, 100 g of copper sulfate and 100 - 120 g of quicklime are taken.
In another bowl, 1 liter of hot water is extinguished by quicklime and the volume is also brought up to 5 l with cold water. The mortar and diluted copper sulfate are individually filtered through a double layer of gauze.
After preparing both liquids, they are mixed by pouring a solution of copper sulphate into milk of lime (NOT REVERSE !!!) and stirring with a wooden stirrer ... When mixing, the solutions should be cold. The mixture should have a beautiful sky blue color and not contain excess copper.
To prepare 10 l of a 3% BORDER LIQUID, take:
- 300 g of copper sulfate
- 300-450 g quicklime
- 10 liters of water.
The discrepancy in the recommended amount of lime is explained by the difference in its quality. High-quality quicklime can only be stored in sealed packaging for a long time. When stored with air, it absorbs carbon dioxide, water and deteriorates ...
In normal BORDEAU LIQUID, there is always an excess of lime. This is due to the fact that the equivalent amount of copper sulphate and lime required to complete the chemical reaction is 1: 3.7. Therefore, there is no need to be afraid that there will be excess lime in the solution.
In addition to the quality of lime, the following factors influence the quality factor of BORDIN LIQUID:
- TEMPERATURE - the colder the solution when draining, the better, because in this case smaller crystals of the chemical are formed;
- WATER DILUTION - the finished Bordeaux liquid must not be diluted with water. Both copper sulfate solution and milk of lime should be brought to a residual consistency before mixing.
To avoid burns to plants, the chemical reaction of the solution must be checked ... You can use a simple way to determine the reaction of Bordeaux liquid - dip the CLEANED IRON SUBJECT (nail, wire, knife blade) into the solution.
The appearance of copper sulfate on the subject of red plaque means that the liquid is not properly prepared. An excess of COPPER SULPHATE is dangerous because it causes plant burns.
Cooked Bordeaux liquid is used on the day of its preparation. During the day, BORDER LIQUID can be saved by adding sugar (5-10 g per 10 l) to it.The use of Bordeaux fluid before infection with pathogens is effective as a preventive measure. Spray the plants evenly over the entire surface of the leaves from the lower and upper sides in small drops.
DO NOT process fruit and berry crops during flowering. Last spraying - 15 days before harvesting.
According to the results of research, 3-4% Bordeaux fluid used in early spring (period of swelling of the kidneys or "the beginning of the dissolution of the kidneys") is highly effective against scab, fruit rot, and claustosporiosis.
Bordeaux tomato mix: instructions for use
Bordeaux mixture is a long-known tool that has found its application in agriculture for the treatment of vegetable crops from fungal diseases.
This drug consists of copper sulfate and lime, diluted with water.
The specificity of the drug is that it is quite toxic, while the negative effect of the drug extends not only to pathogens.
Dosage
To prepare Bordeaux liquid, you must carefully adhere to the established proportion. If you do not have a basic idea of how to dilute the Bordeaux mixture correctly and upset the proportion, you can threaten to destroy absolutely all the beds.
If you plan to prepare a 1% solution, then you should take the same 100 g of copper sulfate for the same amount of water, but add already 150 g of lime. If, for spraying, a tomato needs a 3% Bordeaux mixture, then 300 g of vitriol and 450 g of lime are taken on the traditional 10 l of water.
Expense calculation
For any vegetable crop, including tomato, there is its own optimal dosage of the drug, which is supposed to process the beds or garden plot:
- if you plan to use the solution to protect young fruit trees, then you will need at least 2 liters per tree;
- to process crops that actively bear fruit, you will have to spend at least 10 liters of fluid;
- if you need to spray shrubs, be prepared to spend at least 1.5 liters of solution on one bush;
- for spraying a tomato, you need to prepare 2 liters of liquid per 10 square meters. m beds.
Composition
As already mentioned, it is customary to breed Bordeaux mixture from copper sulfate and lime, in strictly defined proportions.
As we have already said, the ratio of ingredients is of fundamental importance: if the amount of lime is insufficient, you can provoke the occurrence of chemical burns in plants.
Cooking
Despite only two components (water in this case is not taken into account), the preparation of the mixture cannot be called simple: an excessive concentration of active substances can lead to negative consequences for plants, and insufficient - on the contrary, does not have any result.
It is very important to follow the procedure, not to mention the number of components:
- to prepare the solution, use only a non-metallic container;
- in warm water, dilute 10 g of copper sulfate, and mix the solution thoroughly;
- as soon as the substance is completely dissolved, the resulting mixture should be added with cold water so that the total volume of the obtained mixture is 5 l;
- in a separate bowl, you need to dilute about 130 g of hydrated lime per 1 liter of water, thoroughly mixing the resulting substance, until the consistency of liquid sour cream is reached;
- now is the time to add water to the lime mass, so that the final volume is also 5 l;
- after this, the lime solution must be filtered through several layers of gauze (this will help to avoid clogging the device);
- at the end of the cooking process, the solution of copper sulfate is slowly, constantly stirring, poured into a lime solution (in no case, vice versa!).
That's all, the preparation of Bordeaux mixture has come to an end. All that remains to be done is to check the acid reaction of the prepared preparation. For this, it is necessary to lower any metal object into the solution - any nail or piece of wire.
There are several restrictions that must be observed during the preparation of the mixture:
- you can’t change the rules, and pour lime into copper sulfate - this will lead to a significant decrease in the quality of the resulting solution;
- also do not mix components with different temperatures;
- Do not mix together the dry components of the mixture;
- when the solution is completely ready, do not add water to it;
- Do not add vitriol to the prepared lime mortar.
Precautionary measures
As already mentioned, the finished solution can not only protect plants from fungal infections, but also harm the health of both the beds and the gardener himself. Therefore, compliance with the basic safety rules is mandatory:
- use protective equipment when working with the prepared mixture - gloves, respirators, etc .;
- while working with the mixture it is forbidden to smoke, drink liquid or food;
- it is impossible to process the beds located in close proximity to those fruits that are planned to be collected in the next 2-3 weeks;
- do not process plants during the period of active flowering and the formation of ovaries;
- The last processing of your tomatoes with the prepared Bordeaux liquid should be done no later than 2 weeks before the expected harvest.
As the long-standing experience of gardeners shows, despite its venerable age, the Bordeaux mixture is not inferior to its positions in efficiency and popularity among farmers: like decades ago, summer residents continue to choose this tool, remembering its effectiveness and availability.
Bordeaux mixture
Bordeaux mixture is one of the most common fungicides for controlling plant diseases. Bordeaux - is a broad-spectrum fungicide.
Active ingredient: Copper sulfate, at a concentration of 960 g / kg + calcium hydroxide, at a concentration of 900 g / kg. Release form: The drug is produced in the form of a water-soluble 2 component powder.
Purpose of Bordeaux: to protect fruit, vegetables, berries, melons, citrus, ornamental, flower and other crops from a complex of diseases.
Bordeaux fluid is used to combat late blight, coccomycosis, rust, scab, curly and other plant diseases. Bordeaux fluid helps with the main diseases of grapes: mildew, anthracnose, black rot, rubella, cercosporosis.
Mode of application
Do not confuse Bordeaux mixture and Bordeaux liquid! For processing plants use a solution of Bordeaux mixture - Bordeaux liquid, which can be easily prepared at home.
How to prepare a solution of Bordeaux fluid: Bordeaux mixture is a two-component preparation: lime powder and copper sulfate powder. Depending on the season, 1% and 3% Bordeaux solutions are used.
Lime and copper sulfate are bred with water in separate containers. You can take plastic buckets, glass or wooden containers.Do not use metal utensils to prepare the solution! Fluid prepared for spraying should be used immediately after preparation.
Remember: we pour copper sulfate solution into milk of lime !!!
Preparation of a 1% solution of Bordeaux fluid. . Take 100 g of copper sulfate and dissolve in 1 liter of warm water in a wooden or ceramic bowl. When the vitriol is completely dissolved, add another 5 liters of water.
Preparation of a 3% solution of Bordeaux fluid. A 3% solution of Bordeaux fluid is used in the early spring. Take 300 g of copper sulfate and dissolve in 1 liter of warm water (not higher than 50 ° C). Stir the solution until all crystals dissolve. Bring the solution with water to 9 liters.
In another container, dilute 400 g of lime in 1 liter of water.
Wait until the solutions become at the same temperature and slowly, with a thin stream, pour the solution of copper sulfate into the milk of lime (If you do the opposite, the solution will be ineffective).
Period of protective action: 7-12 days. Speed of exposure: no more than 2 hours.
Compatibility with other drugs: Bordeaux mixture is compatible with most pesticides. It is well compatible with systemic fungicides: metalaxyl, oxadixyl, cymoxanil, alet and others, with the exception of preparations containing thiram.
Security measures:
- Hazard class - 2 (hazardous compound).
- Border protection zone for bees over 2 km.
- Phytotoxicity of Bordeaux: in the recommended standards, the drug is not phytotoxic. The possibility of resistance has not been identified.
How to properly process plants
Plant treatment should be carried out in the evening after sunset in calm weather. When processing, it is imperative to use personal protective equipment for the skin, eyes and respiratory organs.
First aid for poisoning:
- If there are signs of poisoning (an unpleasant metallic and astringent taste in the mouth, irritation of the mucous membranes of the nose and throat, excessive salivation, nausea, severe chills), the victim should be taken to fresh air, rinse his mouth with water, change clothes, immediately consult a doctor and present recommendations for use .
- If the product comes into contact with the skin, thoroughly rinse off the preparation with a stream of water, and in case of burns, remove residual lime with mineral or vegetable oil.
- In case of contact with eyes, rinse thoroughly with water, then instill a 0.5% solution of dicaine, continue treatment with an ophthalmologist.
- In case of contact with the respiratory tract, remove the injured person to fresh air, rinse his mouth with water, provide fresh air.
- If it enters the gastrointestinal tract, rinse the stomach with 01% potassium permanganate solution, give the victim a saline laxative (1-2 tbsp.spoon of magnesium sulfate), induce vomiting, and give a diuretic.
The guaranteed shelf life of Bordeaux mixture (dry powders in bags) is 2 years.
Despite the fact that now there are many other fungicides on sale, Bordeaux liquid remains an indispensable assistant to gardeners and gardeners in the fight against plant diseases!
What is Bordeaux mixture
Bordeaux mixture is a composition of two dry components: copper sulfate and calcium oxide,of which Bordeaux liquid is prepared - an aqueous solution for the treatment of garden plants and garden crops from diseases of bacterial and fungal origin.
The chemical formula of the Bordeaux mixture is: CuSO4 • 3Ca (OH) 2. The mechanism of action is pin.
Copper sulfate (aka copper sulfate, it is also the main sulfate copper) acts as a poison - it is toxic to fungi and bacteria due to copper ions - they interact with amino groups and sulfhydryl groups of fungal cell enzymes, causing destruction of the structure of cellular proteins.
Calcium oxide (or quicklime) is extinguished during the preparation process and is used in the mixture as a neutralizer of the strongest oxidizing agent so that the solution does not cause burns in plants.
Advantages and disadvantages of the drug
A solution of Bordeaux fluid quickly comes into contact with the leaves and bark of trees and shrubs, is not washed off by rain. Spraying can be carried out very early in the spring or late in the fall before the buds open (for the first time in February and March with the first thaws).
This pesticide has the longest protective period - up to 30 days. Copper preparations are highly effective against a very wide range of pathogens, pathogens:
- anthracnose
- bacteriosis
- ascochitosis
- coccomycosis
- rubella plums
- root rot
- kleasterosporiosis (hole blotch)
- leaf curls
- macrosporiosis
- melanosis
- mildew
- monilial fruit burn
- olive spotting
- scabs
- percosporellosis
- fruit rot
- spotting
- rust
- septoria
- snow mold
- phylosticosis
- late blight
- cercosporosis
- black rot
Bordeaux fluid deficiencies
Bordeaux liquid is incompatible in tank mixtures with organophosphorus pesticides and any drugs that are destroyed in an alkaline environment.
A certain phytotoxicity is manifested from the regular annual spraying of the garden, in particular during periods of prolonged rainfall. The most phytotoxic copper in the period of active plant growth.
Over the years, copper accumulates in the soil and adversely affects fruit trees and shrubs, causing leaves and ovaries to fall at the beginning of the season.
Copper and its compounds may enter groundwater bodies into nearby water bodies and adversely affect their ecosystem.
Inhalation of dusty particles of copper compounds is especially dangerous, therefore work with Bordeaux mixture should be carried out exclusively in a respirator and in dry, calm weather!
How to cook
What is important to know:
- first, two aqueous solutions are prepared in different containers, i.e. need two containers
- Bordeaux liquid can be diluted exclusively in enameled dishes (without chips), glass, wooden, plastic; it is unacceptable to use aluminum, iron, galvanized dishes
- dissolve the copper powder in hot water, then cool by adding cold, lime - immediately in cold
- mix only cold solutions
- check lime for quality
- the effectiveness of the prepared mixture depends on the ratio of components
What will be needed for the preparation of Bordeaux liquid:
- two buckets: one for 5 liters, the second for 10 liters
- cut gauze for filtering and sieve
- wooden stick for stirring
- iron nail
- kitchen scale accurate to +/- 1 g (if all components are purchased separately, not in a set)
We prepare a 3% solution of Bordeaux fluid
The industry offers us ready-made - suspended and packaged mixtures. There are two plastic bags in the package - one with copper sulfate CuSO 4, the second - quicklime CaO.
To prepare a 3% concentration of Bordeaux liquid in a volume of 10 l, you need to take: 300 g of copper sulfate and 400 g of quicklime (CaO).
- Pour 1 liter of hot water into a 5 liter bucket and fill in copper sulfate, mix well with a stick, then add very cold water to a solution volume of 5 liters.
- We extinguish lime: in a 10-liter bucket we pour 2 liters of cold water and fill in quicklime. Mix well - lime is repaid: CaO + H2O = Ca (OH) 2
- Add cold water to a volume of 5 ml of milk of lime.
- From the first bucket, pour the dissolved copper sulfate in a thin stream into the milk of lime.
- We get 10 liters of a 3% solution of bright blue color, without flakes!
- We check the reaction of the solution: lower the iron nail and look - it should not appear copper plaque.
- We filter the solution through a fine sieve or gauze, folded in 3-4 layers.
- Pour the solution into the sprayer, work.
Bordeaux fluid without errors
The safety of your fruit crops, vegetables and flowers actually depends on the quality of lime.
The correct quicklime (cannon) when extinguished with water will rapidly dissolve with the release of heat (therefore, lime should be bred only with cold water).
The fact that it is necessary to add lime shows the formation of red plaque on a nail - separately prepare a solution of milk of lime and add to the total volume of Bordeaux liquid until repeated tests with a nail show that it remained clean, without red plaque.
If the solution is not corrected, then Bordeaux fluid has an acid reaction and can cause leaf burns.
When adding lime milk, pour it into Bordeaux liquid in a thin stream, evenly stirring the solution with a wooden stick. Initially, we pour the copper solution into lime, and not vice versa!
If you buy a ready-made Bordeaux mixture, then in the set, in addition to copper powder and lime, there is a litmus test. On indicator paper to determine more correctly, because if you shift too much lime, the nail will not be coated with copper, but the solution will reduce the fungicidal properties.
Preparation of a 1% solution of Bordeaux fluid. To prepare 10 l of a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid, you need to take 100 g of copper sulfate and 150 g of lime. The preparation technique is the same as a 3% solution.
When to process
With a solution of 3% concentration, it is permissible to treat trees and shrubs in early spring, until the buds swell, when the green cone of the future leaf has not yet appeared. If the kidneys are already swollen, a 3% solution can burn them!
This is too concentrated solution, after processing the trees are covered with a blue coating, so the treatment is called blue spraying.
If you missed the period of the green cone and the buds started to bloom, it’s better not to risk it and use softer copper-containing products, for example, copper chloride. Too frequent application of Bordeaux mixture or spraying after flowering can cause the formation of a mesh on the fruit and partially falling ovaries.
Secrets of cooking BZ
Bordeaux mixture is packaged and combined in a common package copper sulphate and hydrated lime fluff. Bordeaux mixture is used to make Bordeaux liquid - the best way to combat a number of plant diseases.
In another dish, lime fluff in an amount of 150 g per 5 l of water is dissolved, then the resulting solution of copper sulfate is poured into a solution of lime fluff with a thin stream. Before use, Bordeaux fluid must be filtered through gauze or burlap.
Bordeaux fluid is used:
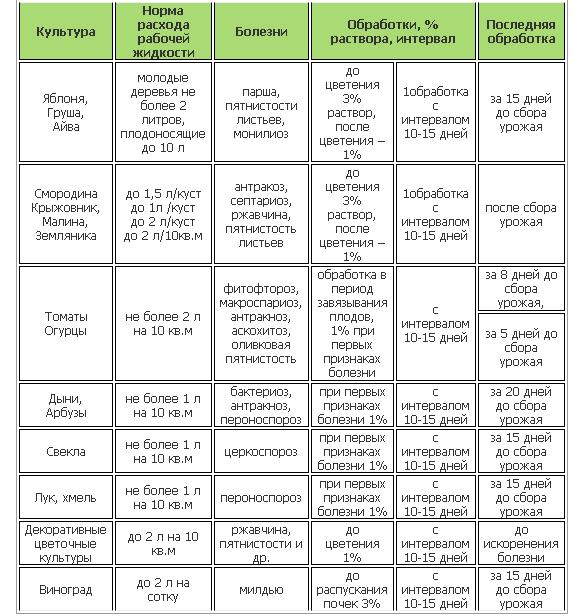
- in a 1 percent concentration for spraying apple and pear - against scab; grapes - against downy mildew (mildew); potato - against potato fungus (phyto fluoride);
- in 0.5-0.75 percent concentration - for spraying vegetable and ornamental plants (cucumbers, tomatoes, left-handed, etc.);
- in 1% concentration for the destruction of eggs and larvae of onion flies; against curl of peach leaves, rust of gooseberry, currant, raspberry and rose, fruit and gray rot of cherry.
Spraying is carried out from manual sprayers (such as "flora", "Avtomaks", etc.).
To process one tree (apple tree) of medium size, 10-16 l of liquid is required; per 100 m2 of planting potatoes or tomatoes or other vegetable plants, 5-10 l of liquid is required.
Spraying of apple trees and pears is carried out at the moment of bud separation, is repeated after the petals fall and when the fruits reach the size of a hazelnut.
When working with Bordeaux fluid, remember that it is toxic to humans and animals. Fruits with traces of spraying before eating should be thoroughly washed. Residues of liquid after spraying should be buried in the ground away from wells.
Sprayed plants should not be fed to livestock. Utensils used for cooking liquids should not be used for cooking. After working with Bordeaux fluid, wash your face and hands with soap and water.
Bordeaux mixture is the best fungicide at all times, but like all fungicides it is good as a warning of the disease and not as a treatment. The correct dilution of the mixture is very important, and especially what is the first to be poured and what is the second, because if you mix it up, the whole solution crystallizes into flakes and you can’t spray it.