Good day! Recently I watched some old horror movie where spiders were the main source of fear.
Pretty creepy sight, I'll tell you! After that, it was somehow scary for the first time to be on the site, because spiders were everywhere in the summer.
So that I would not develop arachnophobia, I decided to closely study the danger of spiders in our area for humans. Want to know what happens if a spider bites? What actions should be taken in such situations? Then read all the details in the material below.
The content of the article:
Spider bite. Symptoms, first aid and treatment
In addition to the pleasant moments in a person’s life that summer brings him — vacation, vacation, beach, fishing, and someone else’s garden, nature sometimes rewards unpleasant “neighbors” that can ruin the summer and sunny mood - spiders.
Okay, if house spiders live in the house, although they can spoil the mood, but when does a poisonous spider occur, such as a karakurt, a tarantula, a hermit spider?
The consequences of a bite of spiders can be very deplorable, even fatal. That is why, it is necessary to arm yourself with the knowledge about the types of some poisonous spiders, the symptoms of their bites and what to do when a spider bites.
Spiders. What are they?
Spiders (lat. Araneae, Aranei) - a detachment of arthropods of the arachnid class. Modern scientists know about 42,000 species of spiders. Almost all of them are predators that feed mainly on various small insects (flies, mosquitoes, midges) and animals (frogs, lizards, small birds). In the territory of the former USSR, about 2900 species of spiders have been studied.
To catch their prey, spiders mainly weave a web, which in some species is silk. When a spider approaches its victim, it bites through it and, along with a bite, poison enters the victim's body. That is why almost all spiders are poisonous, the only difference is the strength and nature of the poison, as well as the strength of the bite.
The hemolytic poison acts mainly on the blood and skin of a person, causing tissue death (necrosis).
Many small spiders are not able to bite through the human skin, so they are not dangerous, but large spiders easily deliver poison to the body.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of a spider bite are:
- growing pain at the site of the bite;
- hyperemia of the skin;
- swelling
- a blister at the site of a bite;
- itching, often throughout the body;
- burning bite;
- muscle pain;
- cramps
- nausea, vomiting is possible;
- indigestion, diarrhea;
- headache, dizziness, fainting;
- possible tachycardia, shortness of breath;
- increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- fever, chills;
- increased salivation, sweating;
- cough, runny nose;
- general weakness, drowsiness.
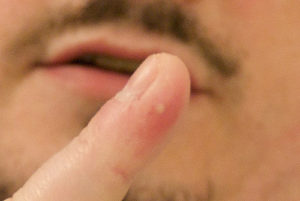
What does it look like
Below are photos with some types of spiders and their bites.





First aid
with a bite of a spider
Proper and qualified help with a spider bite will help to avoid possible complications (paralysis, death), as well as accelerate the recovery of the victim.
First aid for a spider bite includes the following items:
- Keep calm! Thus, it will be much easier to navigate in this situation and make the right decisions.
- Call an ambulance, if not possible, then try to deliver the injured person to a medical facility.
- Put the person down, try to make him move less, because movements accelerate the spread of poison.
- Before the ambulance arrives at the place of the bite, apply a cold compress; the ideal option is ice. Compress will slow the absorption of the poison and its spread throughout the body.
- If the bite fell on one of the limbs, apply a bandage / elastic bandage above it, this will block the poison current in a certain way. Just keep in mind that the bandage should not block the flow of blood, therefore it should not be too tight.
- Drink an antihistamine that will help minimize puffiness, itching and other manifestations of an allergic reaction: “Agistam”, “Suprastin”, “Claritin”, “Loratadin”.
- The patient is injected intravenously with serum against the poison of spiders, after conducting skin tests or fractional sensitization. This serum is usually found at health centers.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Sweet tea will be an excellent remedy.
- With anaphylactic shock (anaphylaxis), it is necessary to begin to provide appropriate assistance - first aid for anaphylactic shock.
In no case should you comb the bite of a spider, because it can make the situation worse!
Bite treatment
After first aid is provided, further treatment is carried out in the hospital, which includes:
- The introduction of serum against the poison of spiders;
- Detoxification therapy. Put droppers with saline. To maintain the electrolyte balance of cells, glucose is introduced.
- The bite site and the surrounding area of the skin are lubricated with anti-inflammatory ointments: Gyoksizon, Kremgen, Prednisolon.
- To strengthen the immune system, vitamin therapy is prescribed.
- With indigestion, frequent diarrhea, a sparing diet is prescribed.
- At elevated temperatures, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed: Paracetamol.
With the bites of such spiders, the hermit spider, with further necrosis of the affected tissues, is treated with special lotions, sanitized, and some time later, after the necrosis zone is clearly identified, it is removed surgically.
Interesting Spider Facts
- Spiders are predominantly nocturnal;
- Some species of spiders can live without food and water for up to several months;
- The largest spider in the world is the spider Galyaf (Theraphosa blondi), which can reach 30 cm in length.
- In the world at the moment, scientists know the only spider that feeds on plant leaves - Bagheera kiplingi.
- The most poisonous and aggressive spider in the world is a banana spider (Phoneutria nigriventer).
- Statisticians note that from 3.5 to 6.1% of the world's population are afraid of spiders. Fear of spiders is called arachnophobia.
Spider bit - what to do
Spiders (arachnids) are silent killers that cause an instant death of their victim in the event of an attack. Patient and prudent arachnids (all spiders belong to this class) weave killer nets from invisible adhesive threads.
All spiders are poisonous. Poisonous glands are located on two head appendages - chelicera. They need poison to kill and digest the victim. The main prey is insects.
In some tropical spiders, the network in diameter reaches 2 m and can even interrupt the flight of a small bird. They feed on frogs, mice, small birds, fish, and even their cousins - cannibalism among spiders is a fairly common occurrence.
Most spiders are not capable of causing significant harm to humans. Although the poison is strong, its small number and poorly developed injection mechanism limit the number of species dangerous to humans.
For people, only those that can pierce the skin are dangerous. The most common species include karakurt (black widow), tarantula, scorpion, hermit spider, cross spider, tarantula spider, domestic spider.
What does a bite look like?
Most spider bites have common characteristics, such as a small bladder (blister) in the middle, swelling and swelling surrounding the site of the bite, and large redness in the form of a circle. On the outside of the bite, the redness is paler.
It is important to note that a spider can only bite once, so if you have several bites, it was probably someone else who did not bite the spider, or several spiders at once. A typical spider bite goes away within a few days and, in most cases, does not require special attention.
However, if the site of the bite looks different - a large bladder appears, bright redness spreading rapidly to the sides, turning blue of large areas of skin - these are serious signs that you need to respond immediately and contact an medical institution urgently.
What to do
First of all, do not panic! Although all spiders look scary, there are only about 12 species whose bite has a serious effect on humans or animals. The two most dangerous are the black widow spider and brown hermits.
Check the wound. After the bite, pay attention to the bite site - whether there is redness, swelling and burning pain. There may be abdominal pain, vomiting, headache, fever, dizziness. The most dangerous reactions are shortness of breath and shock.
Spider identification - if possible and safe. Some spider bites require serious treatment, including antitoxins. If you are unable to identify the spider, this will be helpful in determining the appropriate treatment.
It will help if you can catch a spider in a jar or box (just do not forget about safety). Or at least take a picture of it and show the photo to the doctor.
First aid
- To reduce blood flow in the affected area, it is necessary to fix the arm or leg with a belt or scarf - as in a fracture. This will prevent the rapid spread of poison into the bloodstream and its spread throughout the body.
- Wash the bite with soap and water. Regardless of whether the spider is harmless or poisonous, rinse thoroughly as soon as possible. Even an ordinary spider can, with a bite, infect the wound.
- Apply a cold compress or ice to the bite site.
- Drink plenty of fluids - this will ensure quick elimination of the poison through the kidneys.
- Take a pain medication, such as analgin or ibuprofen.
- As well as an antihistamine that will reduce allergic symptoms - itching, burning, rash.
If you suspect that you have been bitten by a poisonous spider, you can apply a tight bandage above the bite if it is on your arm or leg, making sure that you have not completely stopped blood circulation.
The goal is to slow the spread of poison, and not stop the flow of blood to the limbs. If the bite is on another part of the body, apply a cold and urgently get to a medical facility. Hospitalization is required for most of these types of bites.
Symptoms of bites of different types
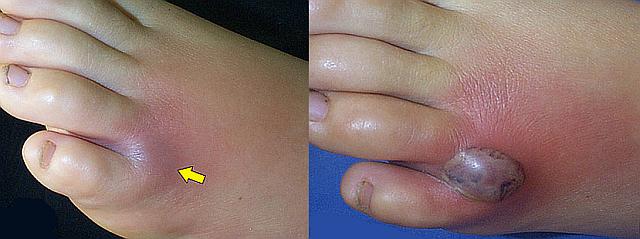
Hermit Spider Bite. One of the four spiders whose bite poses a danger to humans is the hermit spider. A brown hermit is generally not aggressive and generally bites people as a defense mechanism, usually when a person’s leg or arm accidentally gets too close.
Hermit spider venom contains powerful cytotoxins and hemolytic enzymes that destroy red blood cells. Although the bite is usually not painful at the beginning, there is a burning sensation similar to a bee sting during the first few minutes after the bite.
A small white blister may also appear at the site of the bite.
Additional symptoms usually develop between two and eight hours after the bite of a hermit spider. Sometimes it takes up to 12 hours until the symptoms of a bite develop. Signs:
- severe pain at the bite site
- severe itching
- nausea
- vomiting
- fever
- muscle pain
Initially, you can see slight signs of redness at the site of a spider bite.
In most cases, then the skin at the site of the bite hardens, the formation of scar tissue can take several days. More severe local reactions also occur and can cause blistering, discoloration of the skin and necrosis of the skin area.
If possible, you should catch a spider and bring it to a doctor or emergency room for evaluation.
There are no known antidotes for brown hermit bites, so a doctor may prescribe painkillers, antihistamines to relieve itching, or recommend ice bite treatments to reduce pain and swelling.
Cross spider bite. The cross is a small creature harmless to humans, which lives quietly, hunting for insects that fall into their nets. The sharp, poisonous fangs of the cross are primarily a tool for hunting and serve to protect it from other spiders. The victim, falling into the trap, is quickly paralyzed by poison, and then the spider eats it.
The spider looks like a spider rather harmless - it is distinguished by its characteristic pattern of a cross on its back. Color varies from green to gray, depending on the habitat. The cross is very common - it lives almost everywhere.
A person’s bite can only be accidental. Their teeth are not able to damage hard skin, but thinner parts of the body are not a problem. Most often, this situation can occur during a walk in the forest, picking mushrooms or traveling. Crosses grow rapidly and at the end of summer can grow to impressive sizes.
They stretch web canvases between trees at the height of a human face. Inattentive mushroom picker gets into the network being laid and completely destroys it. Then the insect, unwittingly, tries to escape or hides under the clothes. At the moment, we can accidentally crush an insect and then the spider bites.
Sometimes such situations occur during sleep. Spiders are nocturnal creatures and often move in search of good places to hunt. A sleeping person, feeling a slight tingling sensation on his body, instinctively trying to scratch, crushes him, exposing himself to a bite.
The poison of the crosspiece does not cause any harm to man. However, allergy sufferers and toxin-sensitive spiders should consult a doctor.
Tarantula bite (Lycosa, Theraphosidae) poses no danger to humans, but may be accompanied by pain and swelling. The animal after the bite performs a protective maneuver, dropping the hairs from its abdomen. Small hairs, getting into the eyes and skin, cause pain and an urticaria rash. A variety of tarantula is a tarantula spider.
Tarantula spider bite. There are 400 species of tarantulas of different colors. From cobalt blue to gray or dark brown, sometimes black. The tarantula reaches sizes from 9-10 to 17-23 cm, although its body is not more than 10 cm. The rest falls on the legs.
Incredibly, the spider has eight eyes - two in the front and two on the left, right side and back! Usually they dig holes in the ground and build a house there.
Tarantulas are poisonous, but most species of poison are not strong enough to seriously harm anyone.
The bite of a tarantula can be compared with the bites of a wasp or a bee. In most cases, it is harmless, although a person who has an allergy can react like a bee sting.
Recently, some began to get a tarantula spider as a pet. A person’s bite can happen by negligence when trying to escape a spider from a terrarium.
Karakurt bite. Karakurt (Latrodectus tredecimguttatus) - a poisonous spider, lives in Moldova, Crimea, Central Asia. Females are dangerous for humans, who have a pair of tubular poisonous glands located on the upper jaw.
The poisonous segment (chelicera) terminates in a movable sharp claw with an opening in the duct of the poisonous gland. The female has a spherical dense black abdomen with reddish spots. The length of karakurt is about 10 mm.
Symptoms of poisoning by karakurt. After a bite, a small rapidly disappearing speck forms. After 10-20 minutes, severe pain develops at the site of the lesion, which spreads to the abdomen, lower back, and chest.
There is a strong mental arousal, headache, dizziness, suffocation, nausea, vomiting, weakness, shortness of breath, cyanosis, tachycardia, arrhythmia. Strong salivation may begin. Possible respiratory arrest.
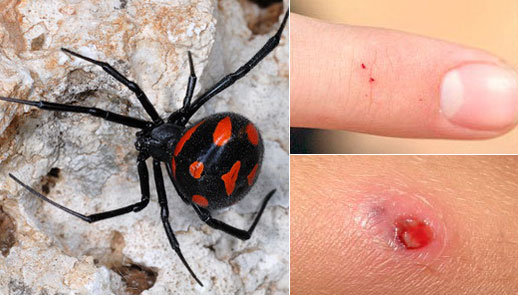
Black widow bite. A spider of the Karakurt species of the genus Latrodectus, the Black Widow (Latrodectus mactans), lives in the USA. Females of this species are very large: the paw span reaches 5 cm, and the body length is 1.5 cm. On the black back there is a red hourglass pattern.
Males are smaller, with a white mark on their backs, the small size of the poisonous apparatus and mild aggressiveness make them almost harmless to humans. Being alarmed, they fall to the ground, tighten their paws and pretend to be dead.
Black widow females are poisonous from the moment they are born. If they guard the laid eggs or feel threatened, they prefer to attack. Spiders use their poison to paralyze the prey, from which they then suck the hemolymph.
Karakurt poison is a protein with a molecular weight of 130,000.Under the action of the poison, ion channels are formed in the presynaptic membranes of nerve cells, through which Ca 2 ++ ions enter the cell.
Under the influence of a toxin, exocytosis of synaptic vesicles is facilitated and the release of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), norepinephrine, acetylcholine is enhanced.
Changes in intracellular homeostasis and an increase in the blood content of biologically active substances affect the functional state of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Karakurt bite, degree. When a black widow bites, there are three degrees of severity of the disease.
- I degree; moderate pain at the site of the bite, there are no general clinical manifestations of intoxication, all laboratory parameters are normal.
- II degree: muscle pain in a bitten limb. Spread of pain on the abdomen with a bite of the foot or on the chest with the bite of a hand. Profuse sweating at the site of the bite. Vital indicators are normal.
- III degree: generalized muscle pain in the back, chest, abdomen. Strong mental agitation. Headache, dizziness, suffocation, nausea, vomiting, weakness, shortness of breath, cyanosis, arterial hypertension, tachycardia, arrhythmia. General profuse sweating. Strong salivation. Possible respiratory arrest. In blood tests, an increase in the content of creatine phosphokinase (CPK), leukocytosis, and proteinuria are noted.
If untreated, the maximum severity of symptoms lasts for 12 hours, the duration of intoxication is 48-72 hours.
Muscle cramps and muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall sometimes cause erroneous diagnosis of peritonitis and the performance of unnecessary laparoscopy.
Scorpion bite. Scorpio (Centruroides sculpturatus) is a poisonous spider widespread in the world. In Russia, lives in the southern latitudes.
Scorpion venom binds to the sodium channels of cell membranes, causing repeated activation of neurons. This is accompanied by an extension of the neuronal action potential in the synapses of the autonomic nervous system, which leads to an increase in blood levels of catecholamines, renin and aldosterone.
Symptoms of poisoning with a scorpion bite. The bite causes severe pain, which quickly spreads along the nerve trunks. The victim screams in pain, sharp weakness develops, cramps of certain muscle groups occur, blood pressure rises, the body becomes covered with cold, sticky sweat.
An urticar rash appears in the bite zone. In severe cases, motor arousal develops, arterial hypertension becomes hypotension, tachyarrhythmia, ventricular extrasystoles, vomiting, profuse sweating, priapism, and salivation occur.
There is a growing visual impairment, ptosis, involuntary contractions of the muscles of the tongue, speech becomes slurred. Within 2-3 hours after the introduction of the poison into the body, breathing is disturbed, pulmonary edema develops. Death occurs with the phenomena of increasing acute cardiovascular and respiratory failure.
When assessing the degree of toxicity of arthropod venom, the following was noted:
- tarantula venom is less toxic than karakurt and scorpion venom;
- the poison of karakurt and scorpion (belongs to toxalbumin) in toxicity exceeds the poison of snakes (~ 15 times). However, fatal poisoning is much less common. This is due to less poison.
Bite treatment
To reduce the spread of poison from the site of the bite throughout the body, immobilization of the limb is indicated. The pain is stopped by novocaine blockade, painkillers are administered: non-narcotic and narcotic analgesics. Cold is applied to the bite area.
Hormones and antihistamines are introduced: blockers of the H1 receptors (promethazine (diprazine), chloropyramine (suprastin), etc. and H2 receptors (cimetidine, ranitidine (acyloquine), etc., vitamins. Benzodiazepines are prescribed for excitation.
When a scorpion bites, Ca-channel blockers, ACE inhibitors are prescribed. Propranolol (anaprilin) effectively and quickly stops tachyarrhythmia, but does not improve hemodynamic parameters. In case of respiratory depression, oxygen is supplied; in the development of acute respiratory failure, artificial lung ventilation (IVL) is performed.
What to do if a spider has bitten: first aid to the victim
These representatives of the arthropod squad can attack an adult and a child, both in the house and in the open. The bites of many spiders will not cause significant harm to a person - a slight redness on the skin will disappear during the day.
But after an attack of a karakurt or a hermit, a severe allergic reaction, swelling of the larynx and respiratory arrest can develop. It depends on the type of arthropod what to do if a spider has bitten, what first aid to give a person.
Spiders attack humans not only in open areas, but also in living quarters
The effect of poison on the human body
Damage to human health depends on the qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the poison secreted by spiders during bites. The larger the specimen, the greater the danger it poses to humans.
Small arthropods are often simply not able to bite through the skin or produce the amount of poison that could harm an adult or baby. But such a statement is true only for representatives of one species.
Tarantulas are larger than karakurt, but their bites do not cause significant harm to humans. But after the attack of a hermit spider, a fatal outcome is quite possible. Depending on the action of toxic compounds, scientists distinguish two types of poison:
- neurotoxic, affecting the central and peripheral nervous system;
- hemolytic, destroying red blood cells after penetration into the bloodstream.
Karakurt and the brown hermit spider are the most dangerous types of arthropods that live in our country. And tourists and experienced travelers can be the victims of attacks by other arthropods anywhere in the world.
Symptomatology
The bites of many, even extremely dangerous spiders, are completely painless. A person who perceives a slight swelling or redness as a scratch and takes no action.
And the symptoms of general intoxication that developed over the course of several hours are very similar to the signs of any bacterial or viral infection. Such a clinical picture of joint bites can be misleading not only the victim, but also the diagnostic doctors.
There are several indirect signs that help a person distinguish a scratch or small wound from a spider bite. After an arthropod attack, the following symptoms occur:
- the bite area gradually swells, and in some cases a pink or red erythema is formed, similar to a thin ring;
- after a few minutes or hours, pain in the limbs occurs, tremors or seizures are possible;
- edema of various localization develops: at the site of the bite, upper half of the trunk or face;
- palpitations, lack of air;
- blood pressure can increase, and then decrease to values that are dangerous to human life.
If the victim has a predisposition to the development of allergic reactions, then large or small red spots form on the skin. They are very itchy and spread rapidly throughout the body. Such symptoms of a spider bite can vary significantly depending on the species of the joint.
After being bitten by a spider spider, the skin turns red and swells quickly.
Karakurt bite
The bite of a karakurt, or “black widow,” is very dangerous for humans. If medical care is not provided, it is very likely to cause death. A person does not feel pain during a bite of a karakurt, which makes it difficult to determine the type of arthropod.
The action of the poison manifests itself within a few hours. In children or people with poor health, this period of time is significantly reduced.
What symptoms occur after a bite of a karakurt:
- sharp pain in damaged tissues after 1-3 hours, a feeling of "goosebumps", redness of the upper layer of the epidermis;
- increased nervous irritability;
- profuse sweating;
- headaches;
- dizziness, inability to stay upright for a long time;
- arterial hypertension;
- the release of a large amount of saliva;
- painful cramps in the epigastric region.
The severity of symptoms is directly dependent on the resistance of the body of an adult or child to the action of the poison. Signs of intoxication persist for several days.
The dangerous consequences of a bite of a karakurt become the formation of ulcerative skin lesions
Tarantula
Many people are mistaken in considering the bite of a tarantula deadly. Undoubtedly, it can cause serious harm to human health, but death is extremely rare. The cause of death is not arthropod venom, but an allergic reaction that develops on its penetration into the body: anaphylactic shock; Quincke's edema.
Within a few minutes, extensive swelling develops on the damaged area of the skin, numerous redness resembling a rash occurs. A person’s arms and legs begin to twitch, blood pressure drops, and dizziness. A characteristic symptom of a tarantula bite is numbness of the limbs.
Hermit Spider Bite
Despite the fact that this species of arthropod does not differ in large size, its bite is deadly even for a strong healthy man. A hermit spider pierces the skin in such a way that a person does not experience the slightest discomfort. The poison enters the systemic circulation and gradually spreads throughout the body. What does a spider bite look like:
- the bite site swells;
- the size of the swelling is rapidly increasing;
- large ulcers form.
If this area of the skin is not treated with antiseptic agents, then after a while the soft tissues begin to ulcerate and die. The clinical picture of intoxication is similar to signs of a respiratory infection:
- aches in bones and joints;
- temperature rise;
- decreased functional activity of the cardiovascular system.
The victim disrupts the functioning of the urinary organs and significantly slows down the metabolism. The heart rate is reduced, there are difficulties with breathing. If at this stage of intoxication the person was not provided with medical care, then he may die.
Cross sting
The poison of this spider is hemolytic. After penetration into the bloodstream under the action of the toxin, red blood cells begin to break down. Since they are responsible for the transfer of molecular oxygen, its deficiency negatively affects the functioning of all human life systems.
Even a large adult cross-breeding creature cannot produce the amount of poison that can cause death. But the bite of a spider gives a person a lot of uncomfortable sensations:
- aching joints, twitching of limbs;
- pain, burning, skin itching in the bite area;
- arterial hypotension, dizziness;
- weakness, apathy, fatigue.
If the victim was not taken to the hospital for detoxification therapy, then the poison will be removed from the body along with feces and urine after 24 hours. For several days, swelling and swelling at the site of the bite will remain.
Home spider
In our country, there are several dozen types of arthropods living in private houses and apartments of high-rise buildings, and they are all quite harmless.
It is difficult to imagine a situation where a domestic spider attacks a person. Such a bite, as a rule, does not cause serious harm to the victim.
Pain arising from skin damage is weak, do not require any pharmacological preparations. A slight swelling disappears without a trace after a couple of days.
The consequences of meeting with arachnids and possible complications
The most serious consequences that develop after bites of any species of spiders include skin infections. The following pathologies are most often diagnosed:
- Arachnoz. After a bite, necrosis of all layers of the epidermis quickly develops. The inflammatory process also affects the subcutaneous tissue and nearby soft tissues located near the damaged area. Necrosis occurs against a background of fever, joint and bone pain, arterial hypotension, heart failure and hemolysis. If medical care is not provided, the probability of death is high;
- Loxoscelism. An infectious lesion of the skin and subcutaneous tissue develops as a result of a bite from a brown hermit spider. Necrosis is rapidly progressing and is characterized by the formation of large ulcers that are difficult to treat. The course of the pathology is complicated by numerous symptoms of general intoxication of the body.
Doctors classify the effects of a spider bite in adults and children as follows:
- mild: hyperemia of the skin, minor pain, swelling, burning sensation and itching;
- moderate: drowsiness, fatigue, tremor of the extremities, indigestion and peristalsis, pain at the site of a bite for several days;
- pronounced: sharp pains spreading throughout the body, cramps, dyspeptic disorders, urination disorders, a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
Strong intoxication with spider poisons occurs in the absence of medical intervention. If medical care is provided on time, then the well-being of the victim quickly improves.
Due to the high permeability of blood vessels in children, poison spreads very quickly in their body, affecting the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
First aid for bites
With bites by spiders of adults or children, severe intoxication of the body develops, so you need to quickly provide first aid to the victim. If a person managed to see the joint and determine its belonging to poisonous species, then medical intervention will be required.
You should call the ambulance team, and only then try to alleviate the condition of the victim. The following measures will help prevent the spread of poison in the body:
- the bite area must be thoroughly rinsed under a stream of cool water using laundry soap;
- if the limb is damaged, it should be immobilized to prevent the penetration of poison into the subcutaneous tissue and healthy tissue sites;
- the bite site must be treated with solutions with antiseptic and antimicrobial activity - hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine bigluconate, iodine, brilliant green, ethyl alcohol, Miramistin, Furacilin;
- you can localize the toxin distribution zone by dragging your arm or leg (without disturbing blood circulation!) with an elastic bandage just above the bite area;
- apply a cold compress to the reddened area of the skin in the form of pieces of ice wrapped in a dense fabric.
If there is a loss of consciousness, then assistance with a spider bite is to monitor the victim until the ambulance arrives. It is necessary to turn a person on his side and make sure that he does not choke on vomit.
In no case should you squeeze out poison from the wound. So you can provoke the rapid spread of poison to neighboring healthy tissues. This will cause necrosis or the rapid formation of purulent ulcerations.
Treatment
If the victim complains of pain in the head or limbs, you need to give him any pain medication that can be found in the home medicine cabinet. The most effective are the following pharmacological preparations:
- analgesics and antispasmodics - Baralgin, Spazmalgon, Maksigan, Spazgan, Analgin;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Nurofen, Nimesil, Nimesulide, Ibufen, Diclofenac;
- preparations with paracetamol - Panadol, Efferalgan.
Acetylsalicylic acid can be given only to the victim of a spider bite in the absence of other drugs. Do not exceed the dosage recommended in the instructions for use in the hope of speeding up recovery.
The victim must also be given any antihistamine drug from the following list:
- Zodak
- Suprastin;
- Claritin;
- Tavegil;
- Tsetrin;
- Diphenhydramine;
- Loratadine.
With a sharp increase in blood pressure, you can normalize the condition with antihypertensive drugs - Enap, Enalapril, Captopril, Indap, Indapamide. And when arterial hypotension occurs, you need to give a person a drink of strong coffee, green or black sweet tea.
A doctor who arrives will examine the victim and hospitalize if necessary. In stationary conditions, detoxification therapy will be carried out using solutions for intravenous infusion. This will quickly remove the poison from the body, prevent serious consequences.
Spider bit: what to do?
The fear of spiders is alive in many people: unaccountable and squeamish, it reminds of the dangers of these insects even when you look at their photos.
Some types of spiders are absolutely safe for humans, but in some cases it can even be fatal.
Summer residents are most at risk, but no one is immune from the attack of dangerous insects, so it is better to know what first aid the victim will need and how to determine the degree of damage, health hazard.
The bite is modified from the type of arthropod, from the amount of poison and other factors. Looking at the wound, one can already say whether the poison is harmful, or the spider was safe.
Harmful bites
The bite site has a round shape, gradually forming a blister with a reddened halo. The consequences of a spider bite in this case can be fatal. The initial symptoms are the same, but a blue halo forms around the blister, and after the blister is damaged, an ulcer forms at the site of the wound.
In some poisonous species, for example, karakurt, it leaves no traces at all. A small red spot appears at the wound site, but then disappears.
Safe Spider Bites
There are several varieties of spiders that most often live in cottages and next to private houses that can bite a person. However, they do not pose a health hazard.
For example, a cross stitch spider bite causes a small swelling of the skin that lasts for 3 days.
The bite of a home spider is also harmless, the only consequences that it can cause are a characteristic itch, as when a bee venom gets under the skin.
Spider bite during pregnancy
Spiders live not only in natural conditions, but also in the house. Indoors, they choose dry and warm places. A bite can happen if you start, for example, cleaning behind a drainpipe or in the mezzanine.
"Home" spiders, as a rule, are harmless to humans, unless the expectant mother has a predisposition to allergic reactions.
This type of arthropod mainly lives on wastelands, slopes of ravines, wormwood. Karakurt migrate, so a bite can occur in the country or in the park. Usually poisonous spiders bite people if disturbed.
Symptoms
The future mother may not even feel that she was bitten by a spider. The bite itself is usually either not felt at all, or it feels like a prick with a needle. You can recognize the bite by a characteristic white spot on the skin, this area is much swollen.
A pink or red rim may form around it. If the spider is not poisonous, then only local reactions are observed - redness, slight bloating. The bite site may itch. These symptoms quickly disappear.
The future mother may experience the following characteristic symptoms:
- muscle pain;
- redness and / or swelling of the face;
- skin rash;
- itching in the body;
- stomach cramps;
- tachycardia.
Symptoms may vary depending on the type of spider. An extensive clinical picture, for example, is observed with a bite of a karakurt. First, local reactions appear: the puncture site hurts (sharp pain), redness appears on the skin, "goose bumps".
After this, there are signs by which you can determine that the poison has begun to act:
- excessive sweating;
- sense of anxiety;
- severe headache or dizziness;
- increased salivation;
- a jump in blood pressure upward;
- nausea (sometimes even vomiting);
- itchy rash;
- dyspnea;
- swelling of the eyelids and limbs;
- cramping of the abdominal muscles, accompanied by pain;
- general weakness.
Such symptoms are observed with the bite of any poisonous spider. A future mother may have all the signs or several characteristic symptoms. The severity of the clinical picture is different: it all depends on the type of poison.
During pregnancy, the body reacts to poison more intensively, because during this period the protective functions are significantly reduced.
Diagnosis of a spider bite during pregnancy
Diagnosis of a spider bite has certain difficulties. If the expectant mother did not see and did not feel the very moment of the bite, then it is difficult to recognize it. Diagnosis is based on severe symptoms. To determine a bite:
- conduct a survey of the expectant mother;
- analyze physical symptoms;
- turn to differential diagnosis.
Complications
In most cases, the bites of domestic spiders are safe, after which complications arise only with individual intolerance to substances that secrete arthropods.
If the expectant mother was bitten by a poisonous spider and at the same time she did not receive timely and adequate first aid, then the consequences can be very serious.
The poison of dangerous spiders can cause necrosis of soft tissues, lead to pathologies of various organs (heart, kidneys, liver), coma and death. If you suspect a bite of a poisonous spider, you must immediately seek medical help, otherwise the consequences can be disastrous.
What can you do
If the expectant mother was bitten by a spider, then she should definitely seek medical help, since there is a high probability that this episode can affect the state of health of the mother herself and the course of pregnancy. If you suspect that the spider was poisonous, first aid measures should be taken:
- wash the bite site with soap and water (this minimizes the risk of infection of the puncture);
- pull the limb above the wound (this will stop the spread of poison throughout the body);
- apply ice to the puncture (it helps to avoid edema);
- drink as much water as possible (liquid helps to remove toxins from the body, reduces the risk of intoxication).
For the relief of concomitant symptoms, antipyretic drugs and antihistamines are used. However, when it comes to the expectant mother, it is recommended to avoid uncontrolled medication. With a bite of a poisonous spider after carrying out emergency preventive measures, the pregnant woman should immediately consult a doctor.
What does the doctor do
The bite of a poisonous spider requires treatment under the supervision of a physician. Therapy in this case depends on which spider has bitten the expectant mother. If it was a karakurt, then the introduction of a special serum is required.
The doctor prescribes treatment depending on the patient's condition and possible risks. Often after a bite, heart and kidney failure appear. In this case, appoint:
- cardiological preparations;
- respiratory analeptics;
- glucorticosteroids.
In the treatment of conditions caused by spider venom, antihistamine and infusion (administration of saline solutions, glucose) therapy give positive results. Adequate measures aimed at neutralizing the poison and restoring the body can avoid the consequences after an arthropod bite.
Prevention
Prevention of a spider bite is reduced to minimize the possibility of contact with arthropods. Since bites usually occur during outdoor recreation, it is recommended to follow simple safety precautions:
- Do not touch spiders and do not disturb them;
- carefully inspect the picnic area;
- Do not wear clothing or shoes outdoors without prior inspection and shaking.
leave a comment